Zero Trust access to apps hosted on-premises or other clouds
Securing on-premises apps and resources with IAP outside of Google Cloud with IAP by deploying IAP Connector. An IAP connector is a Deployment Manager template. When deployed, the template generates resources and routing rules needed to forward IAP-authenticated and IAP-authorized requests to your on-premises app.
The following sections walk through configuring and deploying an IAP connector. IAP targets on-premises apps with the IAP connector. This configurable Cloud Deployment Manager template creates the resources needed to host and deploy the IAP connector into an IAP-enabled Google Cloud project, forwarding authenticated and authorized requests to on-premises apps.
The configurable Cloud Deployment Manager template creates the following resources:
- A Google Kubernetes Engine cluster that maintains Ambassador-based services. Ambassador-based services are built on the Ambassador edge stack, a self-service edge management for Kubernetes to accelerate product delivery with Kubernetes API gateway, delivery accelerator, service preview and developer portal. It provides shared service definitions, reduces testing friction, streamlines continuous integration/continuous development and deploy easily.
- An external HTTP(S) load balancer that acts as the ingress controller for requests.
- Routing rules.
A deployment can have multiple Ambassador-created Compute Engine backend services that run behind one external HTTP(S) load balancer. Each backend service maps to an individual on-premises app.
Once the IAP connector is deployed, IAP secures your app with identity and context based Identity and Access Management (IAM) access policies. Because an IAM access policy is configured on the backend service resource level, you’re able to have different access control lists for each of your on-premises apps. This means only one Google Cloud project is needed to manage access to multiple on-premises apps.
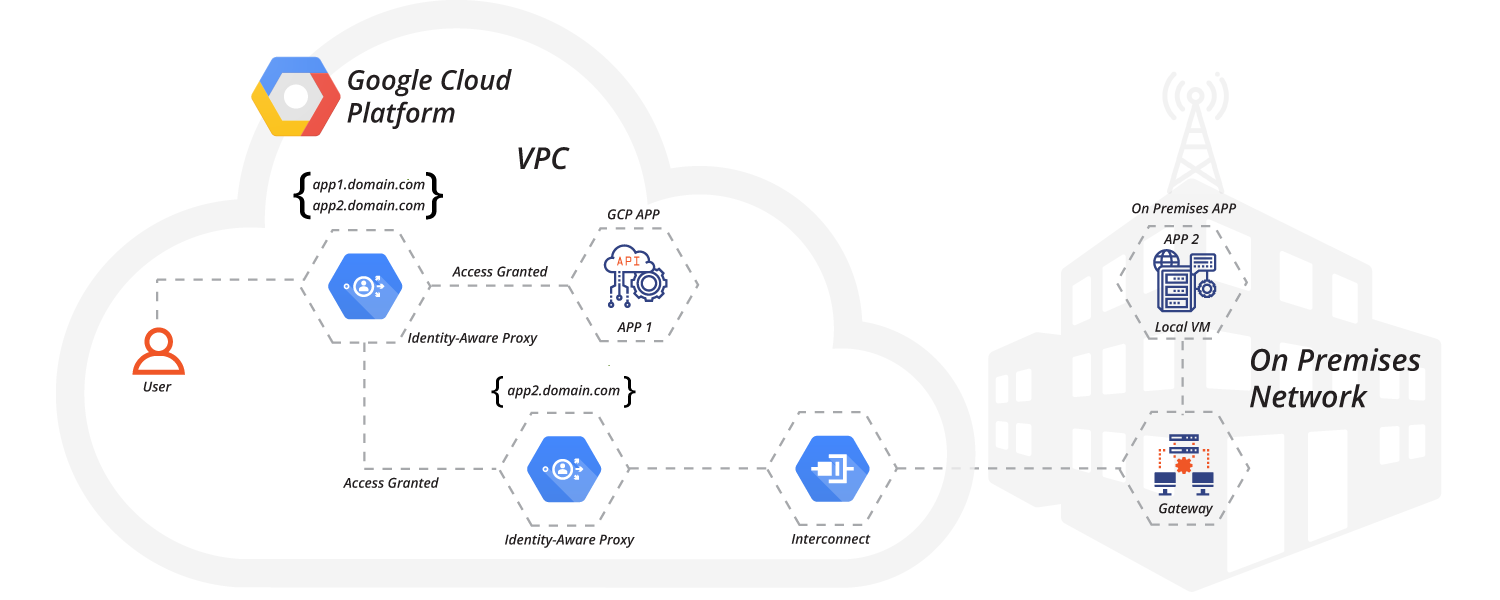
How IAP for on-premises apps works?
When a request is sent to an app hosted on Google Cloud, IAP authenticates and authorizes the user requests. It then grants the user access to the Google Cloud app.
When a request is sent to an on-premises app, IAP authenticates and authorizes the user request. It then routes the request to the IAP connector. The IAP connector forwards the request through a site-to-site connection established with Cloud Interconnect from Google Cloud to the on-premises network.
The exhibit below shows the high-level traffic flow of a web request for a Google Cloud app (app1) and an on-premises app (app2).
Routing rules
When configuring an IAP connector deployment, routing rules are configured. These rules route authenticated and authorized web requests coming to your DNS hostname ingress point to the DNS hostname that’s the destination.
- Each routing name corresponds to a new, Ambassador-created Compute Engine backend service resource.
- The mapping parameter specifies a list of Ambassador routing rules for a backend service.
- The source of a routing rule is mapped to a destination, where source is the URL of requests coming to Google Cloud, and destination is the URL for your on-premises app that IAP routes traffic to after a user has been authorized and authenticated.
Source References:
Securing on premise applications using Google Zero Trust


